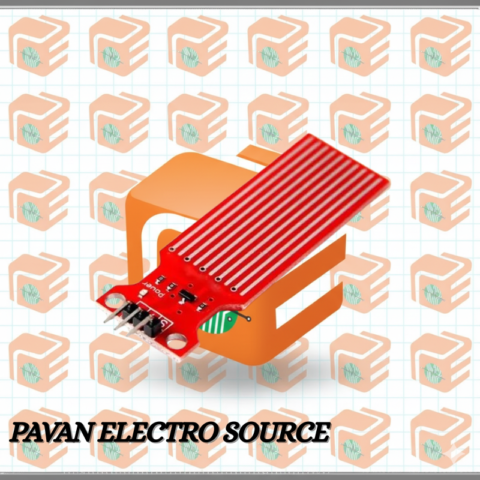
Key Features
• 5-channel infrared reflective sensor array for line tracking
• High-sensitivity IR emitter and phototransistor pair
• Adjustable detection sensitivity via onboard potentiometers
• Compact and lightweight for easy integration on robots or mobile platforms
• LED indicators for visual feedback of each sensor
• Compatible with Arduino, ESP32, Raspberry Pi, and other microcontrollers
Technical Specifications
• Sensor Type: Infrared Reflective Line Tracking
• Operating Voltage: 3.3–5V DC
• Output: Digital signal for each channel
• Detection Distance: Typically 1–15 mm from surface
• Channels: 5 IR emitter-phototransistor pairs
• Interface: 5 digital outputs (DO1–DO5), VCC, GND
• Dimensions: Approx. 65 mm × 12 mm
Applications
• Line-following robots and automated vehicles
• Path detection for mobile platforms
• Obstacle detection and avoidance
• Reflective surface sensing in industrial automation
• Educational robotics and DIY projects
Package Includes
• 1 × TCRT5000L 5-Channel Tracking Sensor Module






There are no reviews yet.